DML GATE Example
DML GATE Example
This notebook demonstrates how to estimate Group Average Treatment Effects (GATE) using Double Machine Learning. GATE allows us to understand treatment effect heterogeneity by estimating the average effect within specific groups defined by covariates.
Mathematical Formulation
Let be the outcome, the binary treatment, and the covariates. We define the Conditional Average Treatment Effect (CATE) as:
\tau(X) = \mathbb{E}[Y(1) - Y(0) \mid X]
For a set of groups (where is an indicator that unit falls into group ), the GATE for group is:
\theta_k = \mathbb{E}[\tau(X) \mid G_k(X)=1]
We will:
- Generate synthetic data with heterogeneous treatment effects.
- Perform Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA).
- Estimate GATEs using
gate_esimandwith both automatic quantile groups and custom user-defined groups.
Generate data
We generate observational data with a nonlinear outcome model, nonlinear treatment assignment, and a heterogeneous (nonlinear) treatment effect .
Ground-truth ATT from the DGP: 1.386
| y | d | tenure_months | avg_sessions_week | spend_last_month | premium_user | urban_resident | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.237316 | 0.0 | 27.656605 | 5.352554 | 72.552568 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| 1 | 5.771469 | 0.0 | 11.520191 | 6.798247 | 188.481287 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 6.374653 | 1.0 | 33.005414 | 2.055459 | 51.040440 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 3 | 2.364177 | 1.0 | 35.286777 | 4.429404 | 166.992239 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 4 | 8.378079 | 0.0 | 0.587578 | 6.658307 | 179.371126 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
EDA

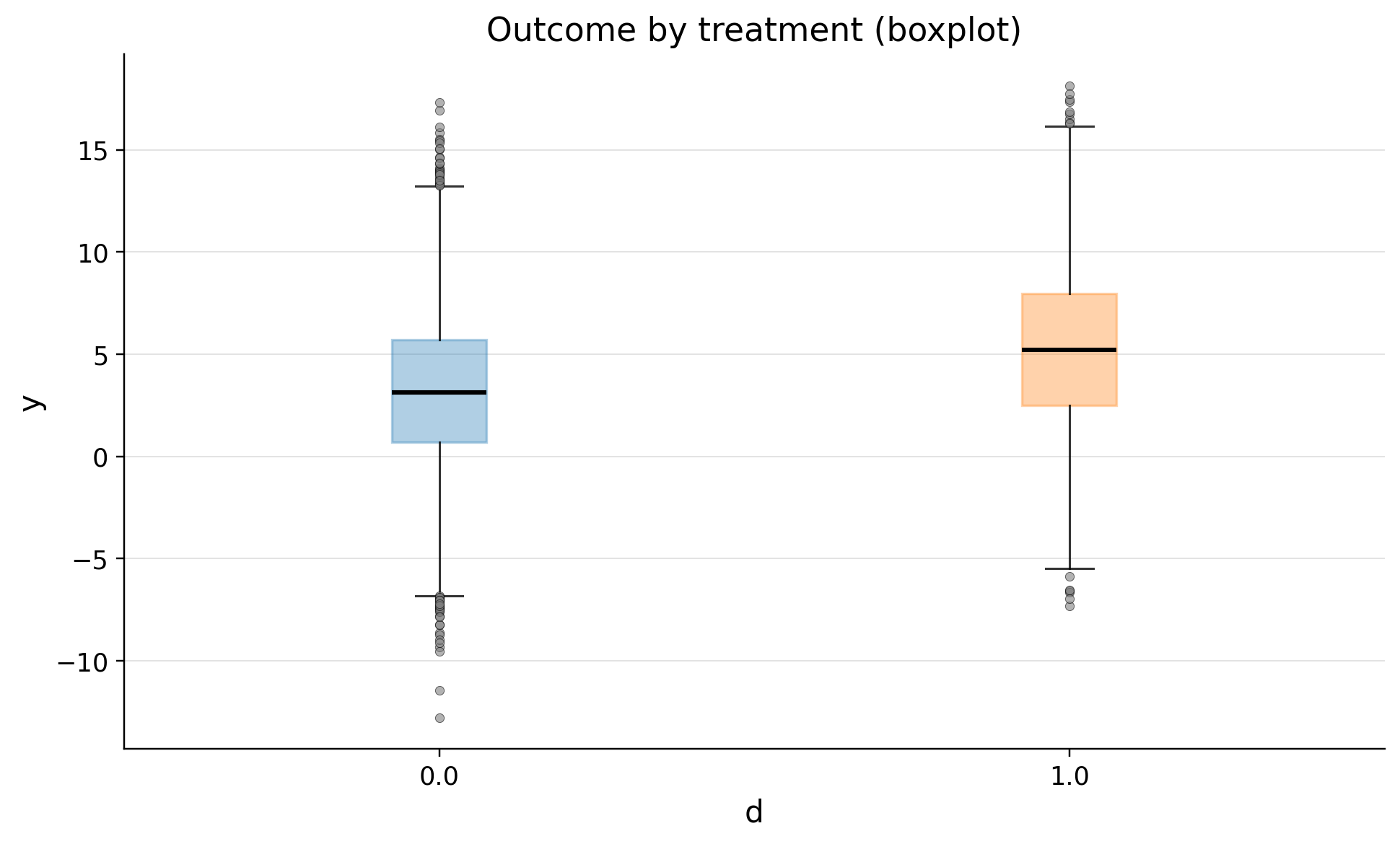
Inference: Estimating GATE
We use gate_esimand to estimate Group Average Treatment Effects.
This function works by leveraging the orthogonal signal from the DoubleML framework.
Methodology
-
Orthogonal Signal: We fit a DoubleML IRM model to obtain a score \psi(W;\hat{\eta}) such that:
\mathbb{E}[\psi(W; \hat{\eta}) \mid X] \approx \tau(X)
where and \hat{\eta} are the estimated nuisance parameters.
-
Best Linear Predictor (BLP): We assume a linear model for the CATE using group indicators :
We estimate coefficients by solving the BLP optimization:
\hat{\theta} = \arg\min_{\theta} \sum_{i=1}^N (\psi(W_i) - \theta^\top G(X_i))^2
When consists of mutually exclusive group indicators, \hat{\theta}_k corresponds to the average of the orthogonal signal within group , providing a consistent estimate of the GATE.
1. GATE by CATE Quantiles
If no groups are provided, gate_esimand automatically creates groups based on quantiles of the estimated CATE (Conditional Average Treatment Effect).
GATE Results (Quantiles):
| group | n | theta | std_error | p_value | ci_lower | ci_upper | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Group_0 | 2000 | 1.376851 | 0.212620 | 9.441200e-11 | 0.960123 | 1.793579 |
| 1 | Group_1 | 2000 | 0.899152 | 0.196052 | 4.512072e-06 | 0.514896 | 1.283408 |
| 2 | Group_2 | 2000 | 1.114911 | 0.194088 | 9.226342e-09 | 0.734507 | 1.495316 |
| 3 | Group_3 | 2000 | 1.190621 | 0.188706 | 2.801072e-10 | 0.820765 | 1.560478 |
| 4 | Group_4 | 2000 | 1.332698 | 0.207103 | 1.235086e-10 | 0.926784 | 1.738612 |
2. GATE by User-Defined Groups
We can also define custom groups based on covariates. For example, let's group users by their tenure:
- < 1 year
- 1-3 years
- > 3 years
GATE Results (Tenure Groups):
| group | n | theta | std_error | p_value | ci_lower | ci_upper | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | tenure_months_1-3y | 6785 | 1.187370 | 0.107453 | 2.189553e-28 | 0.976765 | 1.397974 |
| 1 | tenure_months_<1y | 1649 | 1.231591 | 0.221586 | 2.727795e-08 | 0.797290 | 1.665891 |
| 2 | tenure_months_>3y | 1566 | 1.104541 | 0.221472 | 6.123645e-07 | 0.670464 | 1.538617 |